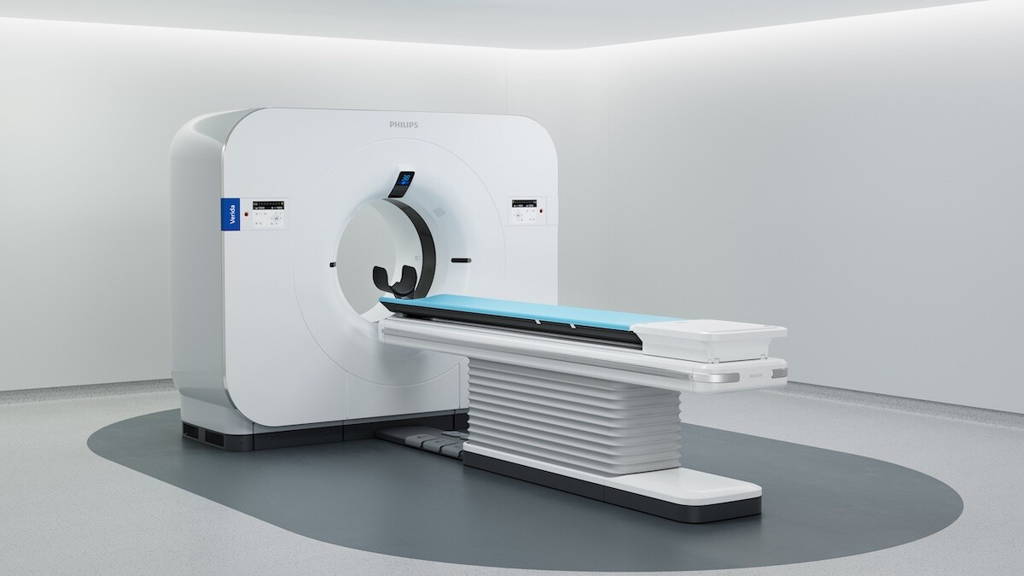
Philips unveiled the Verida spectral CT scanner at the RSNA 2025 trade fair. According to the company, the system is the first detector-based spectral CT scanner that is fully controlled by artificial intelligence. With Verida, Philips aims to automate the entire imaging chain, from acquisition to reconstruction. The company reports that this can reduce noise, improve image quality and speed up steps in the clinical workflow.
Philips presented Verida at RSNA 2025 as a new generation of spectral CT technology. Verida ties in with Philips' software approach to CT scans, which uses AI to make spectral images more accurate. A CT scanner with detector-based spectral measurements “sees more colours” from the X-rays, giving doctors clearer and more accurate images. It also records how tissues absorb different levels of X-ray energy. This should make it possible to distinguish between different materials, unlike conventional CT images.
800+ systems worldwide
According to Philips, more than 800 of the company's spectral CT systems have been installed worldwide, supported by a similar number of peer-reviewed publications. The technology is PACS-native and connects to existing workflows.
With Verida, Philips integrates AI into the entire chain from data acquisition to image reconstruction. The company claims that this leads to lower noise levels and can improve both spectral and conventional images. Philips also reports that the scanner can achieve a significant dose reduction and reduce energy consumption by up to 45 per cent, without affecting image quality, according to the company.
User-friendly platform
‘The clinical benefits of Verida will fundamentally change my approach to cardiac imaging,’ says Prof. Eliseo Vañó Galván, cardiovascular radiologist and head of the CT & MR department at Hospital Nuestra Sra. del Rosario in Madrid, Spain. ‘With more comprehensive insights into each cardiac CT scan, I plan to make spectral imaging routine for all patients, with the goal of building a fully spectral CT department.’ He goes on to say that they evaluated many systems, including photon-counting CT. However, they chose Philips because it offers the precision they need in a user-friendly platform.
According to Vañó Galván, choosing Verida leads to greater diagnostic certainty. Verida also reduces the number of images that require a tube with contrast fluid to be injected into the blood vessels (invasive angiography). This applies not only to cardiology but also to other clinical domains.
Verida gives the CT scanner a significant speed upgrade. The system reconstructs 145 images per second, completing a full examination in less than half a minute. That is more than twice as fast as its predecessors and increases the daily capacity in some departments by around 270 examinations.
AI filters out interference
The technology under the bonnet is just as ambitious. Verida builds on Philips' Spectral Precise Image technology: a smart combination of deep learning algorithms and advanced spectral imaging. The third-generation Nano-panel Precise dual-layer detector does the finer work. With its built-in noise reduction, optimised for AI, it filters interference out of the image.
According to Dan Xu, Business Leader CT at Philips, the new Verida CT system demonstrates what is possible when the latest AI applications are combined with the company's existing spectral CT technology. The system has been developed to further improve both image quality and scan speed and to fit seamlessly into the daily radiology workflow. This should help doctors detect abnormalities earlier, make diagnoses more consistent and support treatment pathways more efficiently based on a single scan. The system will be available in selected markets from 2026.
Co-pilot
We recently wrote about another AI-based innovation from Philips. This is the DeviceGuide, which supports doctors in treating a leaky mitral valve without open-heart surgery. By converting live image data into an intuitive 3D image of the beating heart, DeviceGuide acts as an intelligent co-pilot for doctors, improving visibility, confidence and precision during minimally invasive procedures.